floyd算法
介绍
弗洛伊德(floyd)算法 是解决任意两点间的最短路径的一种算法,可以正确处理有向图或有向图或负权(但不可存在负权回路)的最短路径问题,同时也被用于计算有向图的传递闭包。
(虽然求解多源点最短路径, 可以对每一个点做一次Dijkstre, 但是涉及到而外数据的初始化, 显然这个 的常数是大一点的 =-=, 故可以使用floyd算法)
算法核心
- 状态定义
-
初状态(初始化)
, 即原图
-
状态转移方程
-
[优化: 状态压缩]
因为只用到了 所以可以去掉一个维度
又因为是动态规划, 所以要保证之前的状态全部计算出来, 这就是为什么 是最外层循环的原因.
示例
| ##container## |
|---|
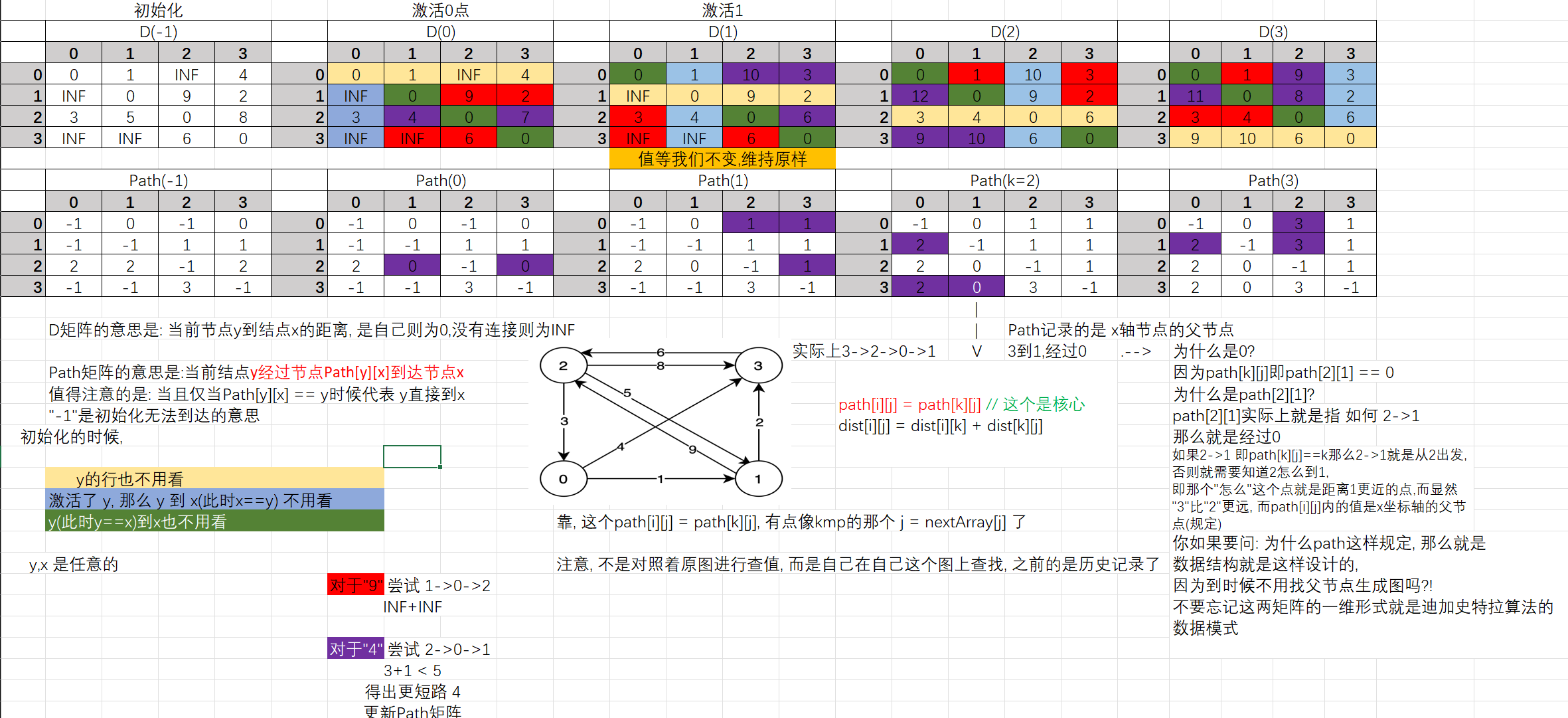 |
代码
竞赛版
好像不能使用链式前向星来存储dp二维数组
如果需要返回的是图, 才需要path数组
const int INF = ((int)1e6);
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
vector<vector<int>> G(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, INF));
for (int i = 0, j, k, w; i < m; ++i) {
scanf("%d %d %d", &j, &k, &w);
G[j][k] = min(G[j][k], w);
G[k][j] = G[j][k];
}
vector<vector<int>> dist(G.begin(), G.end());
for (int k = 1; k <= n; ++k)
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (i == j || i == k || j == k)
continue;
dist[i][j] = min(dist[i][j], dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
printf("%d ", dist[i][j] == INF ? 0 : dist[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
学习版
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define INF 1e6
typedef struct
{
char **show;
int **weight;
int *tagArray; // 用于遍历时候的标记
int add_index;
int number;
} AdjacencyMatrix;
AdjacencyMatrix *initAdjacencyMatrix(int n); // 初始化AdjacencyMatrix
void addAdjacencyMatrix(AdjacencyMatrix *A, char *show); // 添加元素
void connectAdjacencyMatrix(AdjacencyMatrix *A, char *show_1, char *show_2, int weight); // 连接元素
void initTagArray(AdjacencyMatrix *A); // 重置遍历的标记数组 (-1)
void DFS(AdjacencyMatrix *A, int index); // 深度优先遍历
void BFS(AdjacencyMatrix *A); // 广度优先遍历
void freeAdjacencyMatrix(AdjacencyMatrix *A); // 免费
void floyd(AdjacencyMatrix *A); // floyd算法
AdjacencyMatrix *initAdjacencyMatrix(int n)
{
AdjacencyMatrix *A = (AdjacencyMatrix *)malloc(sizeof(AdjacencyMatrix));
if (!A)
{
MALLOC_ERROR:
printf("Malloc ERROR!\n");
return NULL;
}
A->show = (char **)malloc(sizeof(char *) * n);
if (!A->show)
goto MALLOC_ERROR;
A->weight = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int *) * n);
if (!A->weight)
goto MALLOC_ERROR;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
A->weight[i] = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
if (!A->weight[i])
goto MALLOC_ERROR;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
A->weight[i][j] = 0; // 这个是标记数_可改, 记0为未连接
}
A->add_index = 0;
A->number = n;
A->tagArray = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
if (!A->tagArray)
goto MALLOC_ERROR;
initTagArray(A);
return A;
}
void addAdjacencyMatrix(AdjacencyMatrix *A, char *show)
{
if (A->add_index == A->number)
return; // ERROR
A->show[A->add_index++] = show;
}
void initTagArray(AdjacencyMatrix *A)
{
for (int i = 0; i < A->number; ++i)
A->tagArray[i] = -1;
}
void connectAdjacencyMatrix(AdjacencyMatrix *A, char *show_1, char *show_2, int weight)
{
int s_1 = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < A->number; ++i)
{
if (A->show[i] == show_1)
s_1 = i;
}
if (s_1 == -1)
return; // 找不到
int s_2 = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < A->number; ++i)
{
if (A->show[i] == show_2)
s_2 = i;
}
if (s_2 == -1)
return; // 找不到
A->weight[s_1][s_2] = weight;
// A->weight[s_2][s_1] = weight;
}
// 注意遍历的是连通图
void DFS(AdjacencyMatrix *A, int index)
{
printf("%s ", A->show[index]);
A->tagArray[index] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < A->add_index; ++i)
{
if (A->weight[index][i] != 0 && A->tagArray[i] == -1)
{
DFS(A, i);
}
}
}
// 依旧是连通图
// 复杂过头了吧...
void BFS(AdjacencyMatrix *A)
{
// 临时队列
int queue[A->add_index];
int q_h = 0;
int q_t = 0;
printf("%s ", A->show[0]);
A->tagArray[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < A->add_index; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < A->add_index; ++j)
{
if (A->weight[i][j] != 0 && A->tagArray[j] == -1)
{
A->tagArray[j] = 1;
queue[q_t++] = j;
q_t = q_t % A->add_index;
}
}
if (q_h != q_t)
break;
}
while (q_h != q_t)
{
printf("%s ", A->show[queue[q_h]]);
for (int i = 0; i < A->add_index; ++i)
{
if (A->weight[queue[q_h]][i] != 0 && A->tagArray[i] == -1)
{
A->tagArray[q_t == 0 ? A->add_index - 1 : q_t - 1] = 1;
queue[q_t++] = i;
q_t = q_t % A->add_index;
}
}
++q_h;
q_h = q_h % A->add_index;
}
}
void freeAdjacencyMatrix(AdjacencyMatrix *A)
{
free(A->show);
for (int i = 0; i < A->number; ++i)
{
free(A->weight[i]);
}
free(A->weight);
free(A->tagArray);
free(A);
}
static void errorPrint(const char *str)
{
printf(str);
}
void floyd(AdjacencyMatrix *A)
{
// 初始化
int **dist = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int *) * A->number);
if (!dist)
return errorPrint("ERROR Malloc dist!\n");
int **path = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int *) * A->number);
if (!path)
return errorPrint("ERROR Malloc path!\n");
for (int i = 0; i < A->number; ++i)
{
dist[i] = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * A->number);
if (!dist[i])
return errorPrint("ERROR Malloc dist[i]!\n");
path[i] = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * A->number);
if (!path[i])
return errorPrint("ERROR Malloc path[i]!\n");
for (int j = 0; j < A->number; ++j)
{
if (i == j)
dist[i][j] = 0;
else
dist[i][j] = INF;
path[i][j] = -1;
}
}
// 初状态
for (int i = 0; i < A->number; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < A->number; ++j)
{
if (A->weight[i][j])
{
dist[i][j] = A->weight[i][j];
path[i][j] = i;
}
}
}
// *************** v算法核心v ***************
for (int k = 0; k < A->number; ++k) // 动态规划, 每次切换节点
{
// 遍历图(邻接矩阵)
for (int i = 0; i < A->number; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < A->number; ++j)
{
// 一些忽略
if (i == j || i == k || j == k)
continue;
// 状态转移方程
if (dist[i][k] < INF && dist[k][j] < INF &&
dist[i][j] > dist[i][k] + dist[k][j])
{
path[i][j] = path[k][j]; // 从 k 到达节点 j 的路径
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
}
}
}
printf("\n==================================\n");
// 打印
for (int i = 0; i < A->number; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < A->number; ++j)
{
printf("%2d ", dist[i][j]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
}
// 导出就不写了
// *************** ^算法核心^ ***************
// 释放
for (int i = 0; i < A->number; ++i)
{
free(dist[i]);
free(path[i]);
}
free(dist);
free(path);
}
int main(void)
{
// - 动态规划 - 图 - 多原点最短路径 - floyd算法
AdjacencyMatrix *A = initAdjacencyMatrix(4);
addAdjacencyMatrix(A, "v0");
addAdjacencyMatrix(A, "v1");
addAdjacencyMatrix(A, "v2");
addAdjacencyMatrix(A, "v3");
connectAdjacencyMatrix(A, "v0", "v1", 1);
connectAdjacencyMatrix(A, "v0", "v3", 4);
connectAdjacencyMatrix(A, "v1", "v2", 9);
connectAdjacencyMatrix(A, "v1", "v3", 2);
connectAdjacencyMatrix(A, "v2", "v0", 3);
connectAdjacencyMatrix(A, "v2", "v1", 5);
connectAdjacencyMatrix(A, "v2", "v3", 8);
connectAdjacencyMatrix(A, "v3", "v2", 6);
// ************* 开始floyd算法 *************
floyd(A);
freeAdjacencyMatrix(A);
getchar();
return 0;
}
进阶: 动态加边图
addEdge(int[] edge)向边集中添加一条边,其中edge = [from, to, edgeCost]。数据保证添加这条边之前对应的两个节点之间没有有向边。
向图中添加一条边,如何维护 数组?
最暴力的做法是,每次添加一条边,就用 时间全部重算一遍。有没有更快的做法呢?
解决
对于 ,记 , 。如果 ,则无法更新任何点对的最短路。否则枚举所有 ,尝试看看能否更新成更小,即从 到 的如下路径
是否更短,写成式子就是
注意: 当 或 时,我们需要用到 这样的值,所以初始化的时候, 要置为 。
对于 ,返回 即可。
答疑
问: 在 中,上式 的计算依赖于 的值,如果先计算 ,再计算 ,我们还需要重新计算 吗?
答: 没有必要,每个 只需要计算一次。如果 因为 这条边变小,说明从 到 的最短路包含 这条边。那么对于 ,最短路不可能是 ,这意味着最短路会经过 这条边两次。所以重新计算 是不可能让 变小的。
代码:
class Graph {
const int INF = INT_MAX / 3;
vector<vector<int>> f;
public:
Graph(int n, vector<vector<int>> &edges) : f(n, vector<int>(n, INF)) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
f[i][i] = 0;
}
for (auto &e : edges) {
f[e[0]][e[1]] = e[2]; // 添加一条边(题目保证没有重边和自环)
}
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (f[i][k] == INF) continue;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[i][k] + f[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
void addEdge(vector<int> e) {
int x = e[0], y = e[1], w = e[2], n = f.size();
if (w >= f[x][y]) { // 无需更新
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[i][x] + w + f[y][j]);
}
}
}
int shortestPath(int start, int end) {
int ans = f[start][end];
return ans < INF ? ans : -1;
}
};
// 作者:灵茶山艾府
// 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-graph-with-shortest-path-calculator/solutions/2229013/dijkstra-suan-fa-mo-ban-pythonjavacgo-by-unmv/
// 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
// 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。

