线索二叉树
背景介绍
-
现有一棵结点数目为
n的二叉树,采用二叉链表的形式存储,对于每个结点均有指向左右孩子的两个指针域。 -
结点为
n的二叉树一共有n-1条有效分支路径。那么,则二叉链表中存在2n -(n-1)= n+1个空指针域. 那么,这些空指针造成了空间浪费。
| ##container## |
|---|
 |
-
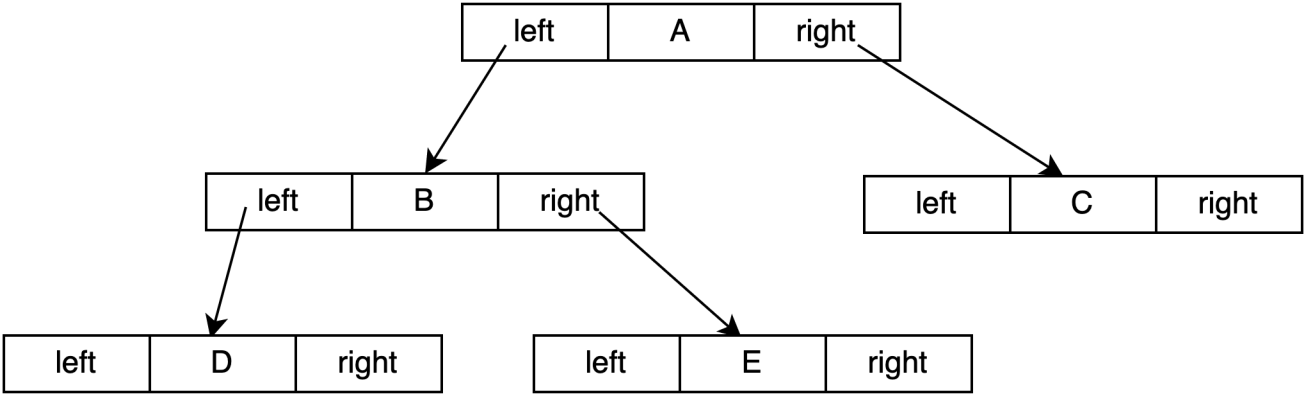
当对二叉树进行中序遍历时可以得到二叉树的中序序列。
-
如图所示二叉树的中序遍历结果为DBEAC,可以得知A的前驱结点为E,后继结点为C。
-
这种关系的获得是建立在完成遍历后得到的,那么可不可以在建立二叉树时就记录下前驱后继的关系呢,那么在后续寻找前驱结点和后继结点时将大大提升效率。
线索化
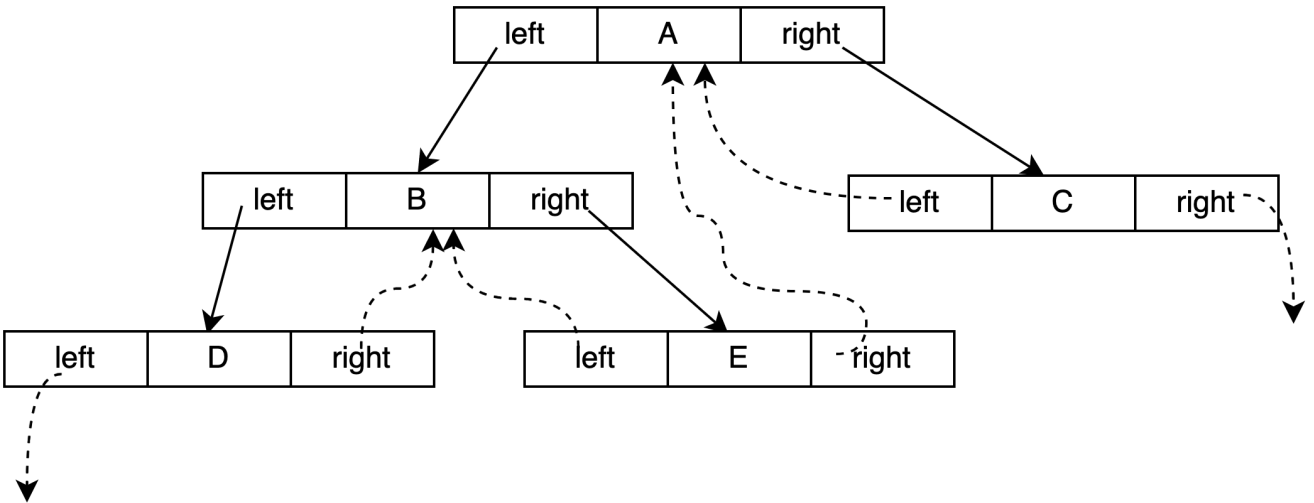
- 将某结点的空指针域指向该结点的前驱后继,定义规则如下:
- 若结点的左子树为空,则该结点的左孩子指针指向其前驱结点。
- 若结点的右子树为空,则该结点的右孩子指针指向其后继结点。
- 这种指向前驱和后继的指针称为线索。将一棵普通二叉树以某种次序遍历,并添加线索的过程称为线索化。
| ##container## |
|---|
 |
线索化的改进
- 可以将一棵二叉树线索化为一棵线索二叉树,那么新的问题产生了。我们如何区分一个结点的
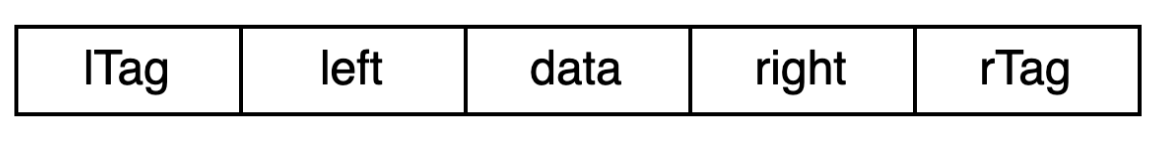
lchild指针是指向左孩子还是前驱结点呢? - 为了解决这一问题,现需要添加标志位ltag,rtag。并定义规则如下:
ltag为0时,指向左孩子,为1时指向前驱rtag为0时,指向右孩子,为1时指向后继
| ##container## |
|---|
 |
- 在遍历过程中,如果当前结点没有左孩子,需要将该结点的
lchild指针指向遍历过程中的前一个结点,所以在遍历过程中,设置一个指针(名为pre),时刻指向当前访问结点的前一个结点。
线索化的优势
递归遍历需要使用系统栈,非递归遍历需要使用内存中的空间来帮助遍历,而线索化之后就不需要这些辅助了,直接可以像遍历数组一样遍历。
线索二叉树核心目的在于加快查找结点的前驱和后继的速度。如果不使用线索的话,当查找一个结点的前驱与后继需要从根节点开始遍历,当然,如果二叉树数据量较小时,可能线索化之后作用不大,但是当数据量很大时,线索化所带来的性能提升就会比较明显。
代码实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef char Element;
typedef struct _B_tree_node
{
Element data;
/* 线索化特有的, 为 0 则是普通的数, 为 1 则是线索化的了*/
_Bool Ltag;
_Bool Rtag;
struct _B_tree_node *left; // 左子树
struct _B_tree_node *right; // 右子树
} BTreeNode;
typedef struct
{
BTreeNode *root; // 树根
int nodeNum; // 结点数
int tag; // <状态>线索化特有的
/*
* 定义:
* 0 为未线索化
* 1 为前序线索化
* 2 为中序线索化
* 3 为后序线索化
* 4 为层序线索化
* */
} BTree;
BTree *binaryTreeInitialization(BTreeNode *root); // 初始化树头
BTreeNode *addBinaryTreeNode(Element e); // 创建一个节点
void linkNodeToBinaryTree(BTree *T, BTreeNode *F, BTreeNode *L, BTreeNode *R); // 链接节点
void inOrderThreadedTree(BTree *T); // 线索化 <递归>
void inOrderTree(BTree *T); // 中序遍历 <线索化版本>
// void inOrderTree(BTree *T); // 线索化后的遍历 (不需要递归)
void freeBinaryTree_TagTOW(BTree **T); // 释放树 <线索化版本>
void text_01(void); // 用于测试代码
BTree *binaryTreeInitialization(BTreeNode *root)
{
BTree *T = (BTree *)malloc(sizeof(BTree));
if (!T)
{
printf("TREE_ROOT malloc Error!\n");
return NULL;
}
T->nodeNum = 0;
T->root = root;
T->tag = 0;
return T;
}
BTreeNode *addBinaryTreeNode(Element e)
{
BTreeNode *node = (BTreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(BTreeNode));
if (!node)
{
printf("TREE_NODE malloc Error!\n");
return NULL;
}
node->data = e;
node->Ltag = node->Rtag = 0;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
void linkNodeToBinaryTree(BTree *T, BTreeNode *F, BTreeNode *L, BTreeNode *R)
{
if (!F)
{
printf("[Error]: Parent Is NULL!\n");
return;
}
if (L)
++T->nodeNum;
if (R)
++T->nodeNum;
F->left = L;
F->right = R;
}
static BTreeNode *pre = NULL; // 私域全局变量 - 小弟: 始终跟在node指针后面
static void zhong_xui_bian_li(BTreeNode *node) // 私域函数 <链接属性为只能在本文件中 访问 || 使用 >
{
if (node)
{
zhong_xui_bian_li(node->left);
// 中节点
if (!node->left) // 指向前驱结点
{
node->left = pre;
node->Ltag = 1;
}
if (pre && !pre->right) // 指向后继结点
{
pre->right = node;
pre->Rtag = 1;
}
pre = node; // 注意! 这个是全局变量, 在下面这个语句的上下是有区别的!!!
// 在上是指中, 在下是去完才指中(慢了!)
zhong_xui_bian_li(node->right);
}
}
void inOrderThreadedTree(BTree *T)
{
/* 这个是一个递归的中序线索化qwq */
if (T->tag != 0)
{
printf("[Error]: The Tree 线索过了!\n");
return;
}
zhong_xui_bian_li(T->root);
T->tag = 2;
}
void inOrderTree(BTree *T)
{
// 中序遍历
if (T->tag != 2)
{
printf("[Error]: The Tree 中序线索了吗!\n");
return;
}
BTreeNode *node = T->root;
while (node)
{
// 1. 左
while (!node->Ltag)
{
node = node->left;
}
printf("%c ", node->data);
// 2. 回溯<到达中节点>输出再往右
while (node->Rtag && node->right)
{
node = node->right;
printf("%c ", node->data);
}
node = node->right;
}
}
void freeBinaryTree_TagTOW(BTree **T)
{
if ((*T)->tag != 2)
{
printf("[Error]: The Tree 中序线索了吗!\n");
return;
}
BTreeNode *node = (*T)->root;
BTreeNode *Free_node = NULL;
while (node)
{
// 1. 左
while (!node->Ltag)
{
node = node->left;
}
Free_node = node;
// 2. 回溯<到达中节点>输出再往右
while (node->Rtag && node->right)
{
node = node->right;
free(Free_node);
Free_node = node;
}
node = node->right;
free(Free_node);
}
free(*T);
*T = NULL;
}
/* 当然忽略 0 1, 采用后序遍历进行删除也可以 */
// static void freeTreeNode(ThreadedBTree *tree, TreeNode *node) {
// if (node) {
// if (node->lTag == 0)
// freeTreeNode(tree, node->left);
// if (node->rTag ==0)
// freeTreeNode(tree, node->right);
// free(node);
// --tree->count;
// }
// }
void text_01(void)
{
// 创建结点
BTreeNode *T_a = addBinaryTreeNode('A');
BTreeNode *T_b = addBinaryTreeNode('B');
BTreeNode *T_c = addBinaryTreeNode('C');
BTreeNode *T_d = addBinaryTreeNode('D');
BTreeNode *T_e = addBinaryTreeNode('E');
BTree *T_head = binaryTreeInitialization(T_a);
linkNodeToBinaryTree(T_head, T_a, T_b, T_c);
linkNodeToBinaryTree(T_head, T_b, T_d, T_e);
inOrderThreadedTree(T_head);
inOrderTree(T_head);
freeBinaryTree_TagTOW(&T_head);
}
int main(void)
{
// 二叉链表 - 中序线索二叉树 - 实践版
/*
* 线索化
* 将某结点的空指针域指向该结点的前驱后继,定义规则如下:
* 若结点的左⼦树为空,则该结点的左孩⼦指针指向其前驱结点。
* 若结点的右⼦树为空,则该结点的右孩⼦指针指向其后继结点。
*
* ltag为0时,指向左孩⼦,为1时指向前驱
* rtag为0时,指向右孩⼦,为1时指向后继
*
* 遍历过程中,如果当前结点没有左孩⼦,需要将该结点的 lchild 指针指向遍历过程中的前⼀个结点,
* 所以在遍历过程中,设置⼀个指针(名为 pre ),时刻指向当前访问结点的前⼀个结点。
**/
text_01();
return 0;
}

