Linux进程相关指令
查看父子进程
ps -ef: 以全格式显示当前的所有进程,查看进行的父进程.
-e: 显示所有进程-f: 全格式显示
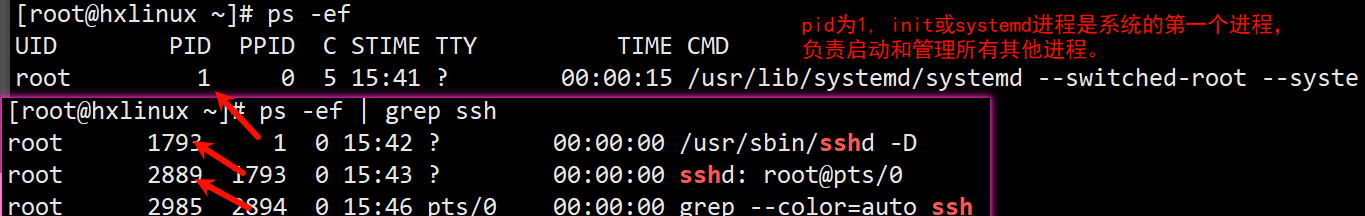
示例: 查看指定进程信息(使用了grep过滤)
ssh为管理远程连接的进程
[root@hxlinux ~]# ps -ef | grep ssh
# 所属用户 进程id 父进程id 占用 时间
root 1793 1 0 15:42 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D
root 2889 1793 0 15:43 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/0
root 2985 2894 0 15:46 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto ssh
| ##container## |
|---|
 |
终止进程
若是某个进程执行一半需要停止时候,或是已经消耗了很大的系统资源时候,可以考虑停止该线程。
基本语法:
kill [选项] [pid] # 过进程号杀死/终止进程。
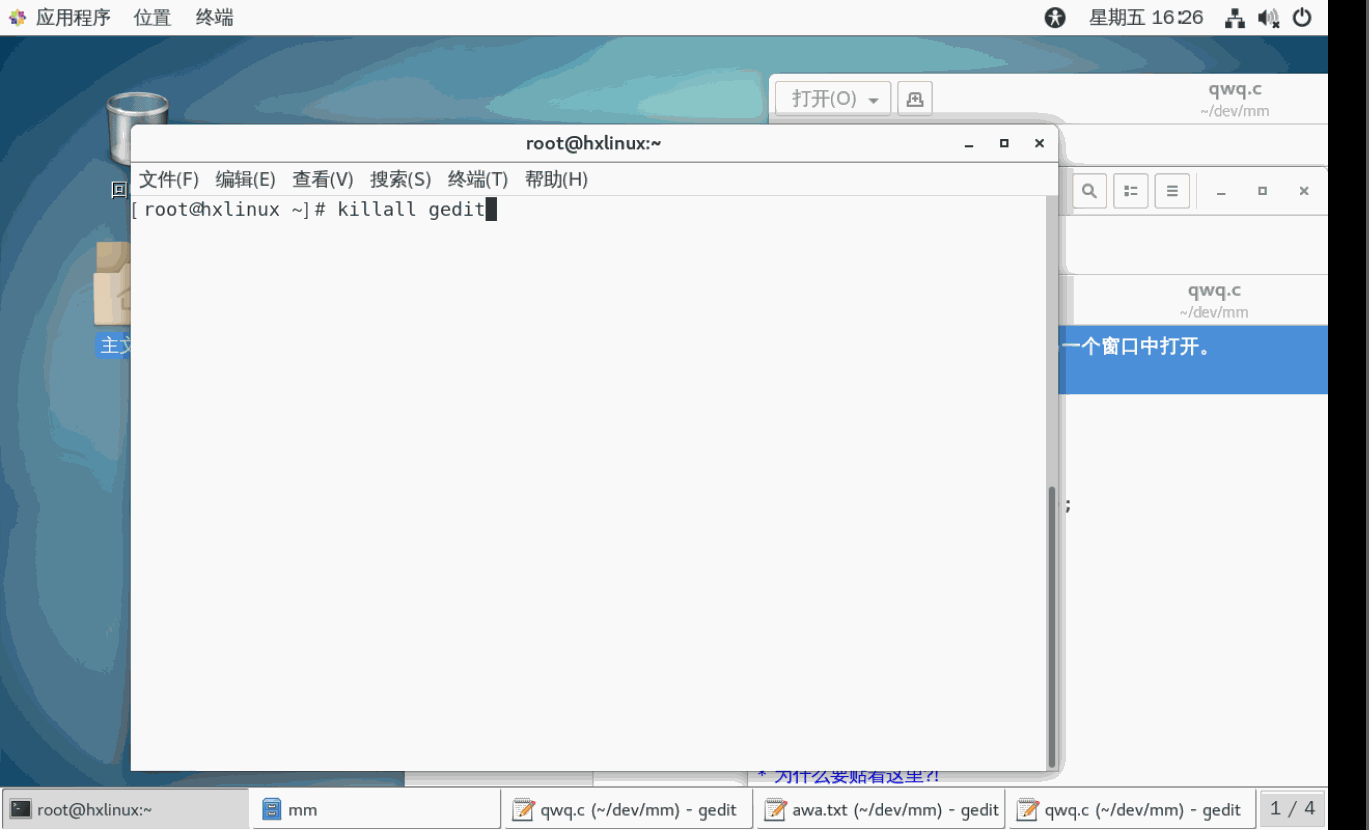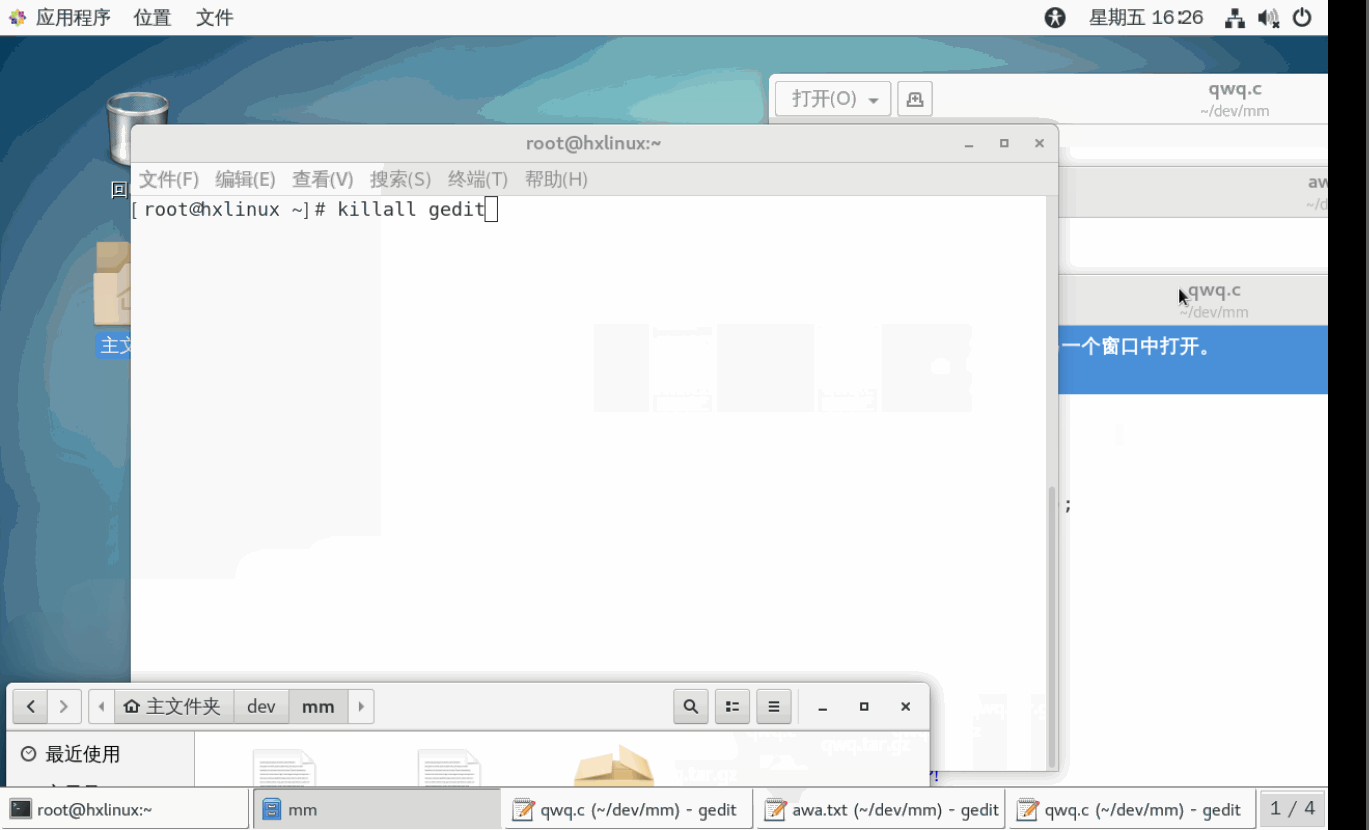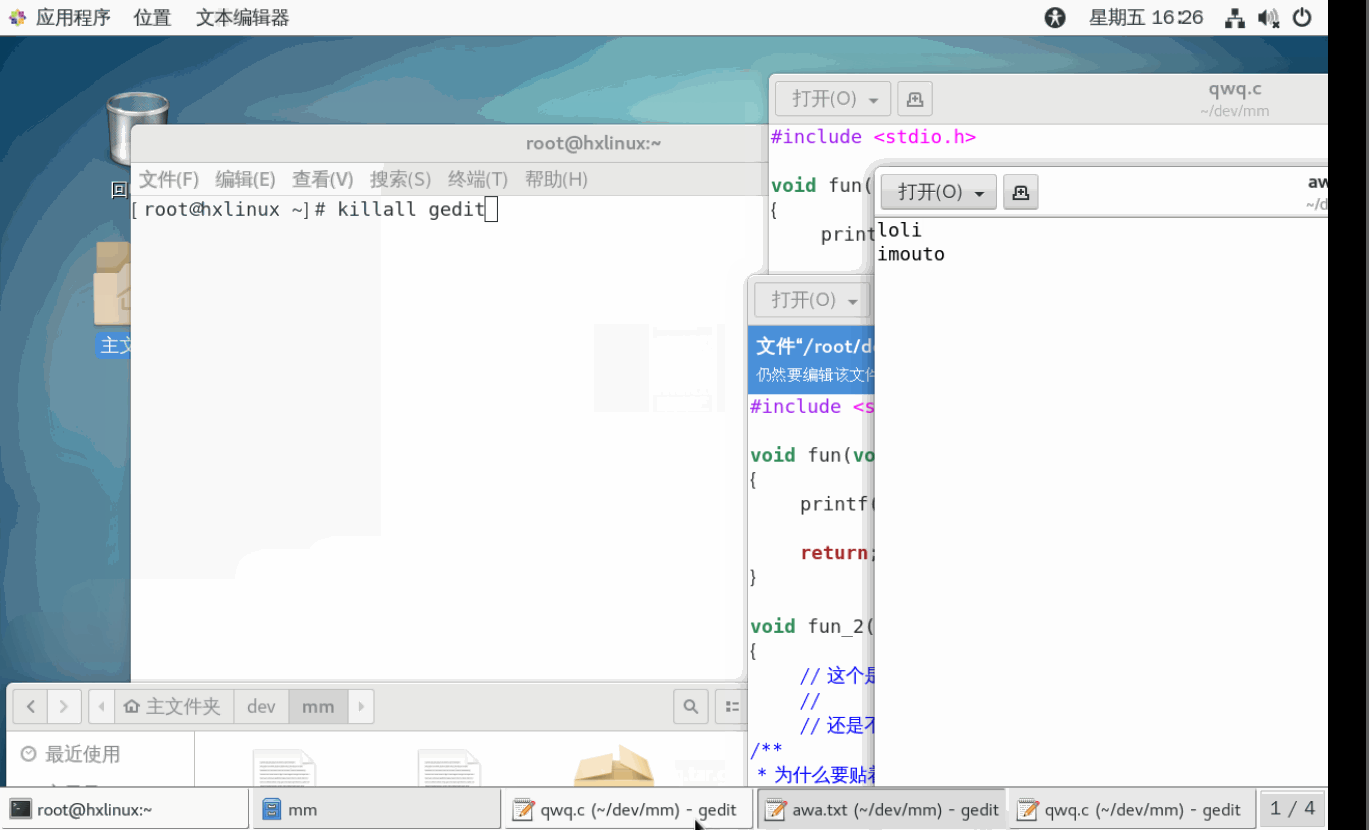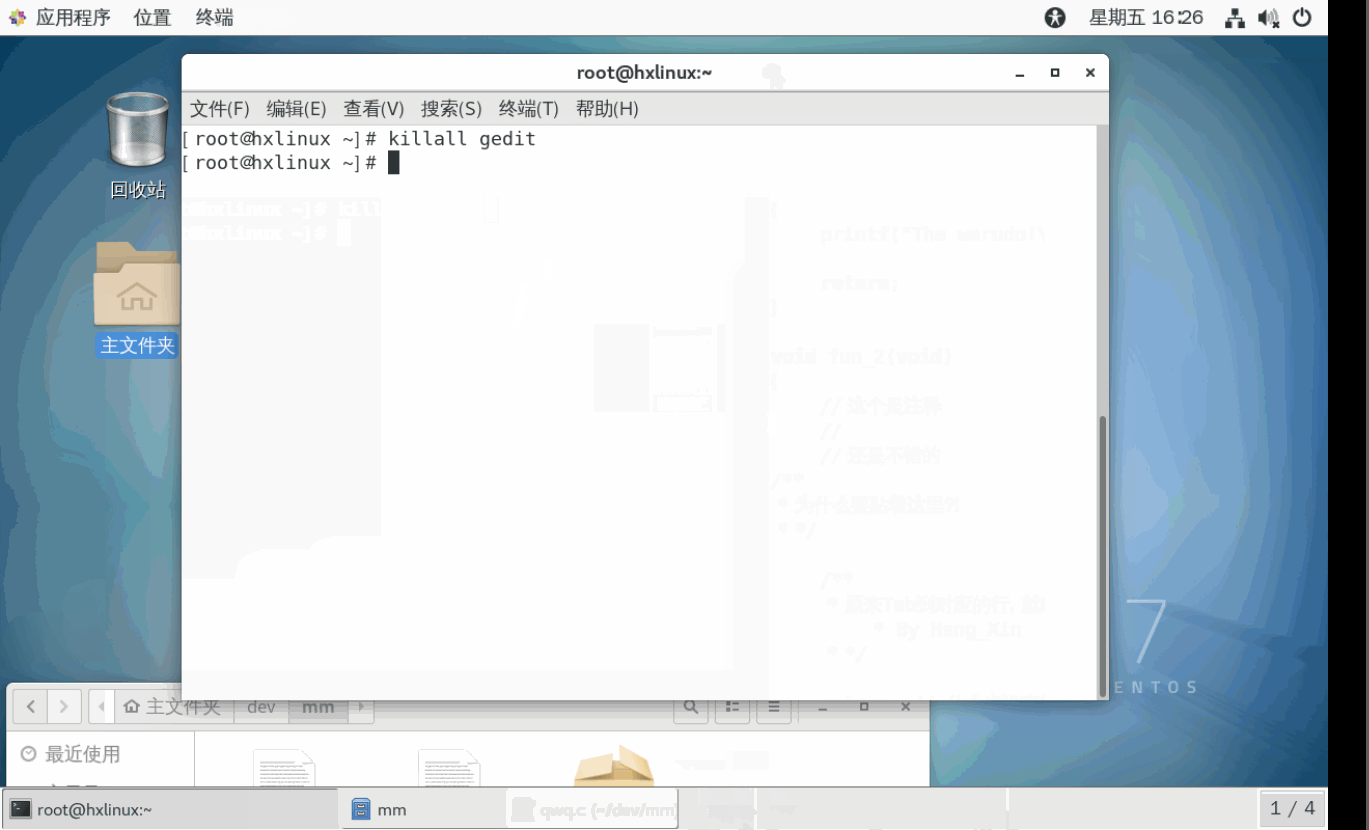
killall # 会杀死当前进程和其子进程。
常用选项:
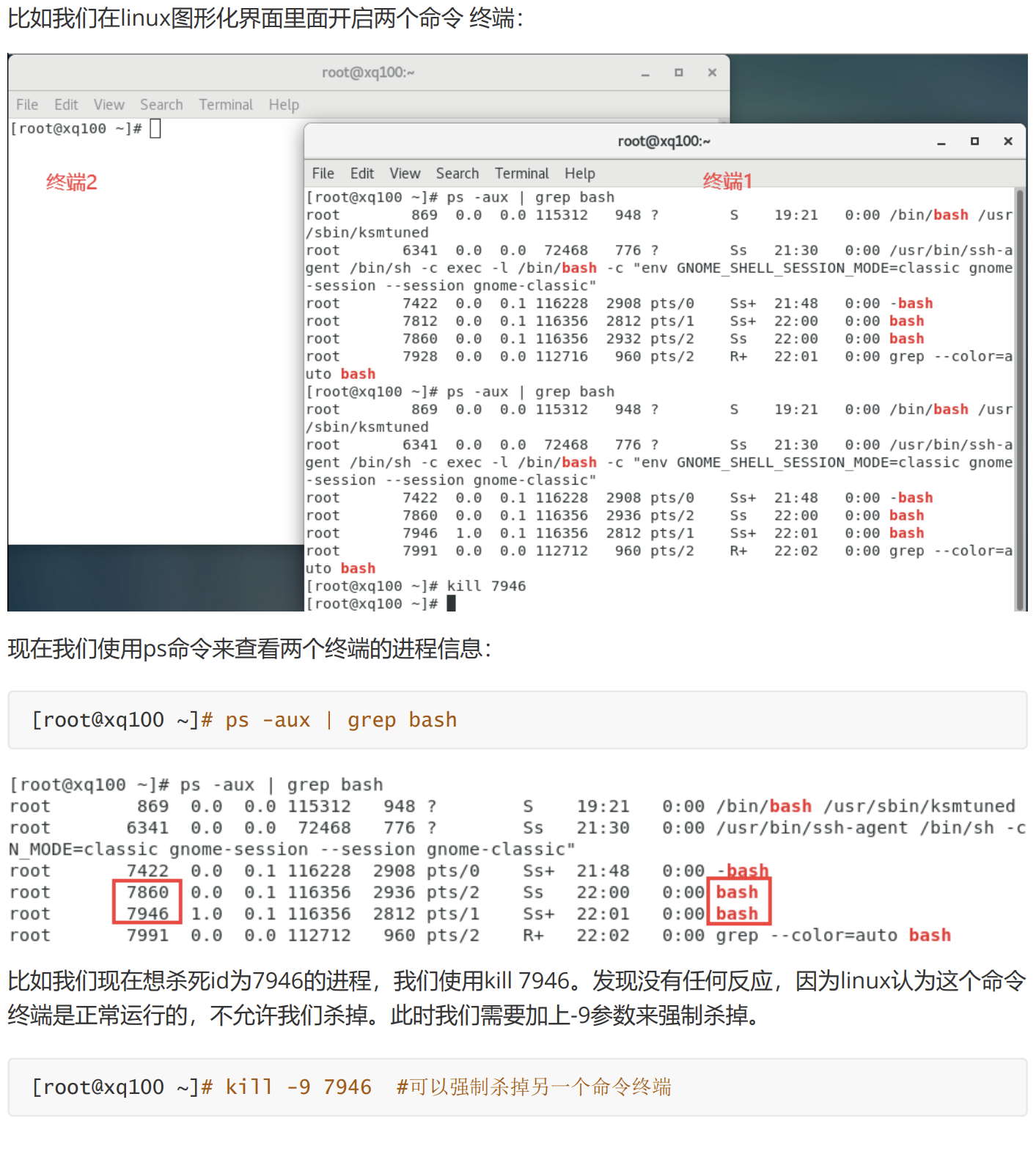
-9: 表示强迫进程立即停止
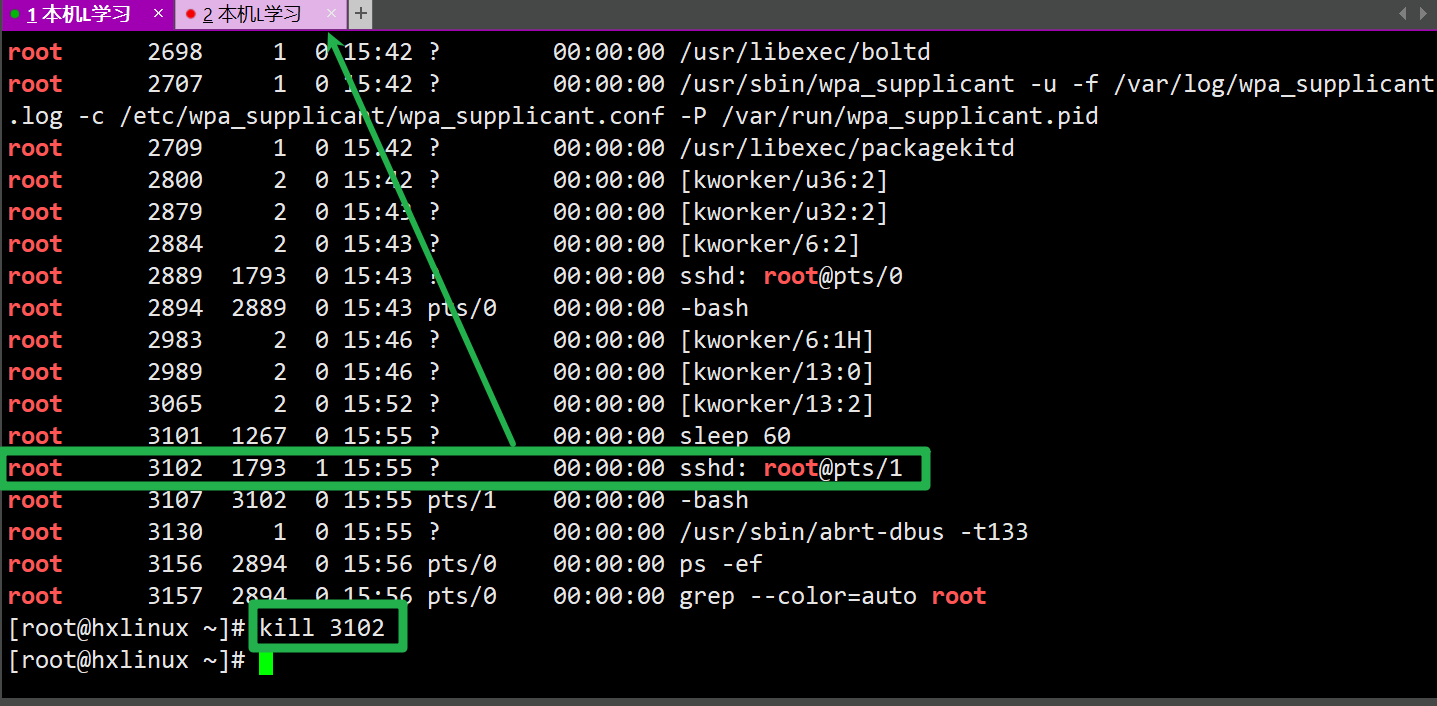
示例1: 终止远程用户链接:
| ##container## |
|---|
 |
示例2: 终止远程登录服务sshd。不允许远程登录。然后重启sshd服务,允许远程登录。
| ##container## |
|---|
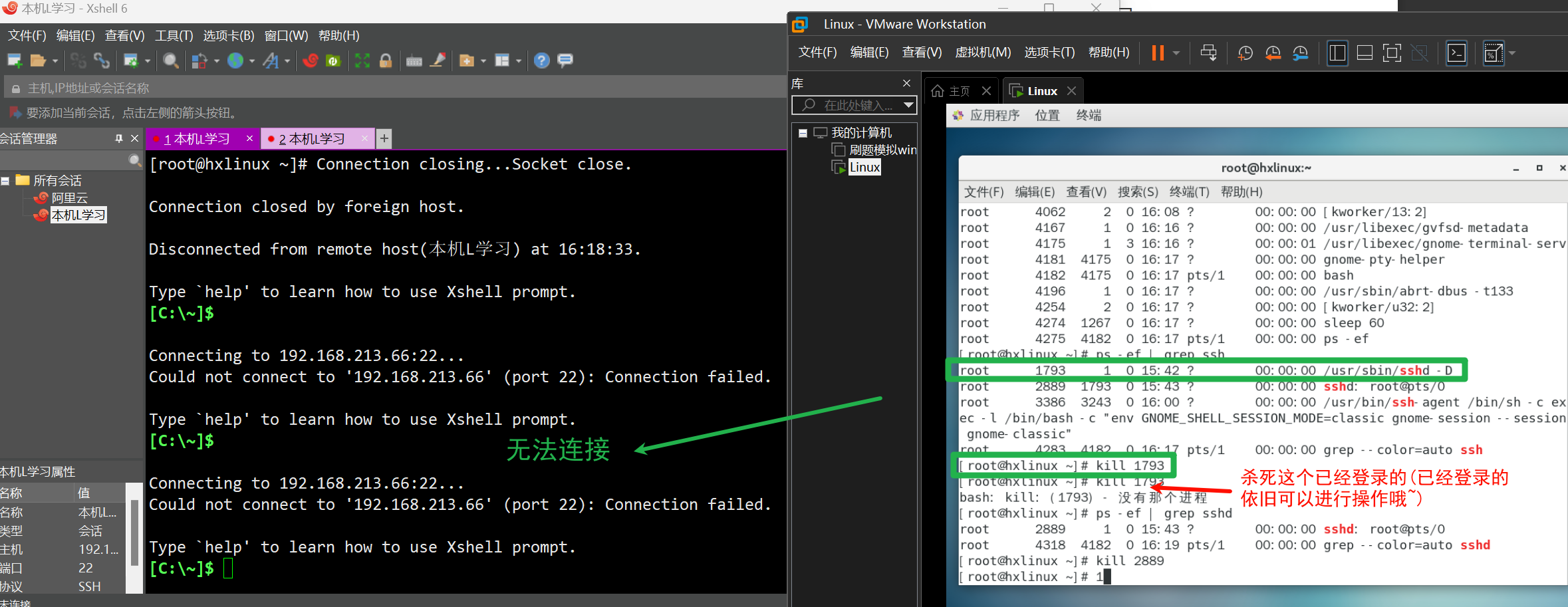 |
此时我们可以使用/bin/systemctl start sshd.service重启ssd服务,这样就可以再次远程登录了。
[root@hxlinux ~]# /bin/systemctl start sshd.service
[root@hxlinux ~]# ps -ef | grep sshd
root 4435 1 1 16:23 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D
root 4443 4182 0 16:23 pts/1 00:00:00 grep --color=auto sshd
示例3: 终止多个gedit(记事本打开文件的进程),演示killall.
| ##container## |
|---|
 |
示例4: 强制杀死
| ##container## |
|---|
 |

