maven分模块开发与设计
聚合工程
| ##container## |
|---|
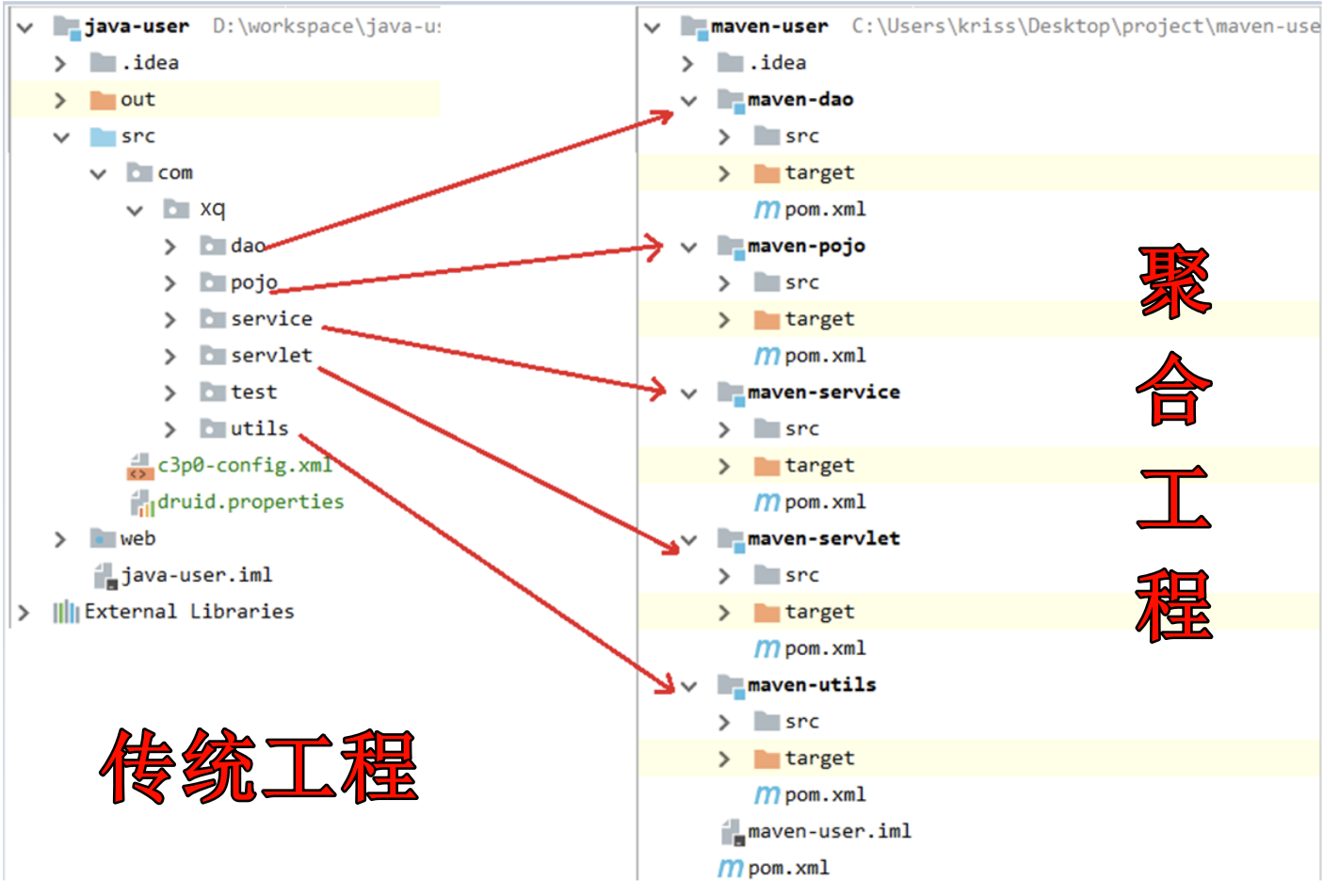 |
| 传统工程与聚合工程对比 |
实际上, 以后的学习和工作中, 我们都是使用 聚合工程.
不要看它结构好像很复杂, 就觉得不好用, 实际上好处大大滴有:
- 方便管理:聚合工程的目录清晰,父工程可以集中管理依赖包,对版本进行统一控制。
- 快速开发:在父工程中执行构建命令,子工程会自动构建,加快开发流程。
- 模块化结构(解耦):将一个项目的多个功能模块分开,然后再对每个模块进行横向切分,例如三层架构中的web层、service层和dao层,使项目结构更加清晰。
- 统一依赖版本管理:通过
dependencyManagement标签,父工程可以指定jar的版本信息,子工程中引用父工程的依赖信息时,可以省略版本号,具体版本号由父工程指定.
实例
创建父工程
使用maven创建一个父工程。在POM里面导入相关依赖:
<dependencies>
<!-- servlet依赖的jar包start -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- servlet依赖的jar包start -->
<!-- jsp依赖jar包start -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- jsp依赖jar包end -->
<!--jstl标签依赖的jar包start -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
<!--<scope>provided</scope>-->
</dependency>
<!-- JSTL实现包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>taglibs-standard-impl</artifactId>
<version>1.2.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--jstl标签依赖的jar包end -->
<dependency>
<groupId>c3p0</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--beanUtils的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-beanutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-beanutils</artifactId>
<version>1.8.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--dbutils组件 封装了原生的jdbc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-dbutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbutils</artifactId>
<version>1.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--logging-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.18</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<configuration>
<port>8088</port>
<path>/</path>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
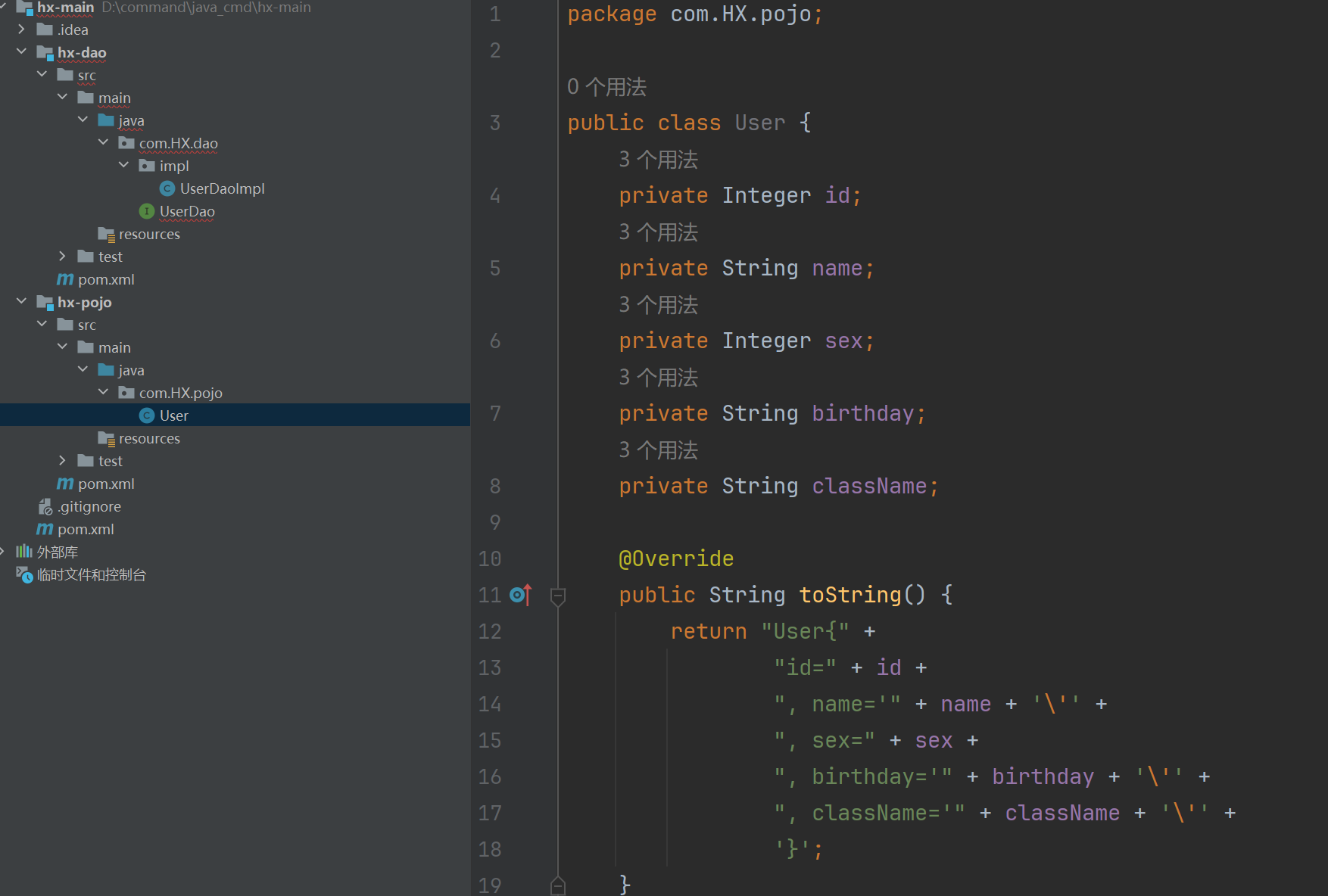
hx-pojo
在父工程上,右键,新建模块(使用maven构建,不使用骨架创建)。然后创建实体类
| ##container## |
|---|
 |
hx-utils
在父工程上,右键,新建模块(使用maven构建,不使用骨架创建)。然后创建工具类类
package com.HX.utils;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 创建连接数据库的类
*/
public class DataSourceConfig {
/**
* 需要在c3p0-config.xml进行配置
*/
static ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
/**
* 获取数据源的方法
* @return
*/
public static ComboPooledDataSource getDataSource() {
return dataSource;
}
/**
* 获取连接对象
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return dataSource.getConnection();
}
}
c3p0-config.xml内容: (请放到资源文件夹)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<c3p0-config>
<default-config>
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/hx_demo</property>
<property name="user">root</property>
<property name="password">root</property>
<!--
初始化的连接数量 在连接池里面初始化10个连接对象
-->
<property name="initialPoolSize">10</property>
<!--
最大空闲时间
某一个连接对象空闲时长最多是30s,超过了30s,该连接对象会被自动回收
-->
<property name="maxIdleTime">30</property>
<!--
最大连接数量
在连接池里面存在最多的连接数量
-->
<property name="maxPoolSize">100</property>
<!--
最小连接数量
-->
<property name="minPoolSize">10</property>
</default-config>
</c3p0-config>
hx-dao
在父工程上,右键,新建模块(使用maven构建,不使用骨架创建)。然后创建接口以及实现类。
- pom文件
- 由于这个模块需要用到实体类,操作数据库也需要用到工具类。所以dao模块需要依赖
pojo和utils模块
- 由于这个模块需要用到实体类,操作数据库也需要用到工具类。所以dao模块需要依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.HX</groupId>
<artifactId>hx-pojo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.HX</groupId>
<artifactId>hx-utils</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
| ##container## |
|---|
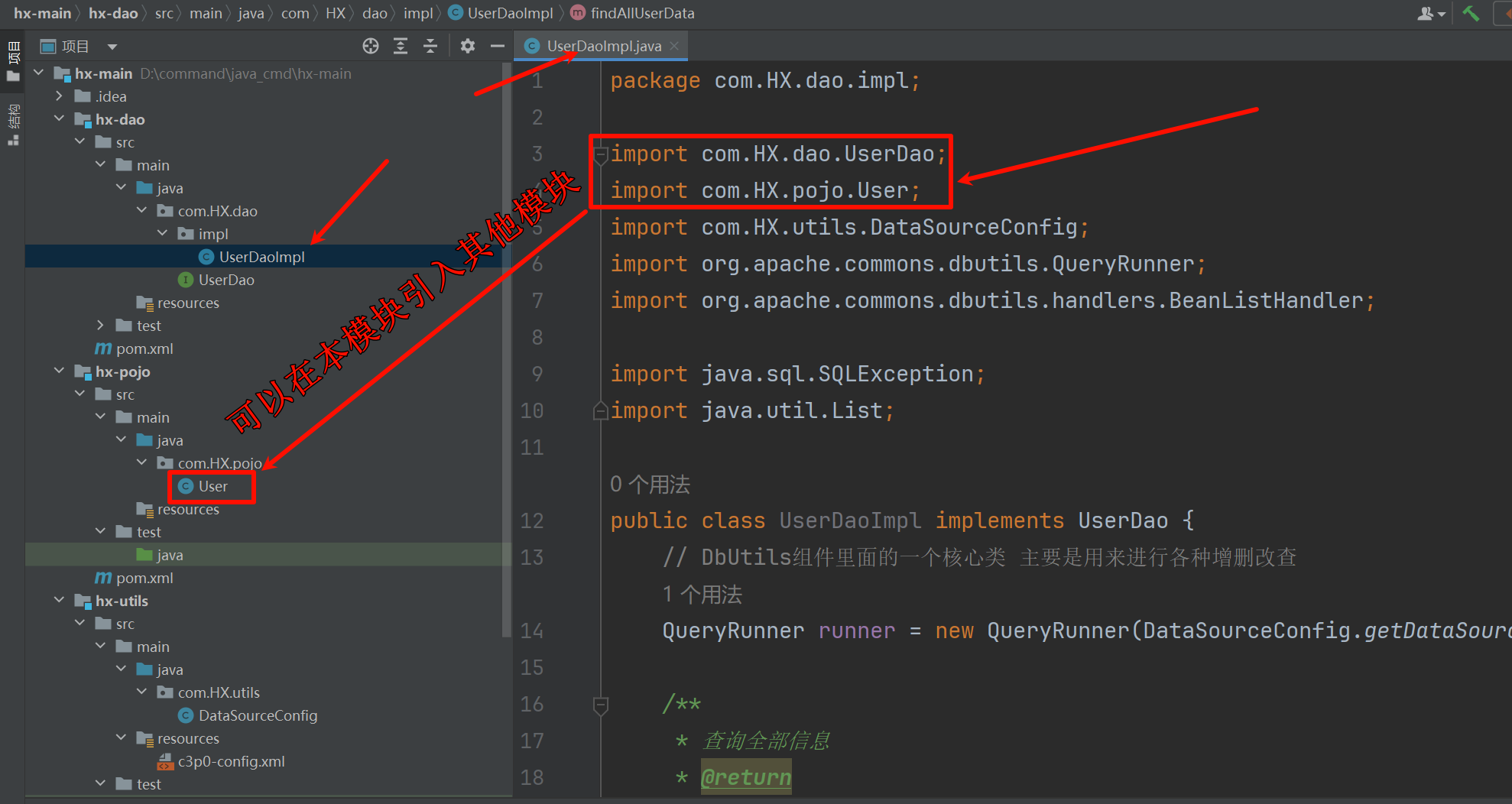 |
package com.HX.dao.impl;
import com.HX.dao.UserDao;
import com.HX.pojo.User;
import com.HX.utils.DataSourceConfig;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
// DbUtils组件里面的一个核心类 主要是用来进行各种增删改查 (类似于对jdbc的封装)
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner(DataSourceConfig.getDataSource());
/**
* 查询全部信息
* @return
*/
@Override
public List<User> findAllUserData() {
String sql = "select id, name, sex, birthday, className from stu where id < ?";
try {
List<User> query = runner.query(sql, 10, new BeanListHandler<User>(User.class));
return query;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
hx-service
在父工程上,右键,新建模块(使用maven构建,不使用骨架创建)。然后创建业务接口以及实现类。
- pom文件
- 由于service模块需要调用dao模块里面的数据。所以service模块依赖dao模块。
- 而dao模块已经导入了pojo和工具类的依赖, 那么service模块也会继承
- 由于service模块需要调用dao模块里面的数据。所以service模块依赖dao模块。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.HX</groupId>
<artifactId>hx-dao</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
hx-servlet
在父工程上,右键,新建模块(使用maven构建,使用骨架创建)。然后创建servlet
servlet依赖service,请自行配置pom, 这里不多赘述
package com.HX.servlet;
import com.HX.service.UserService;
import com.HX.service.impl.UserServiceImpl;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
@WebServlet("/say")
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter writer = resp.getWriter();
writer.print("<h1>Hello this is say.jsp desu!</h1>");
UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
writer.print(userService.findAllUserData());
writer.flush();
writer.close();
}
}
然后在插件处启动tomcat-run即可, 如果不行, 请在父目录的pom那里启动
聚合与继承
聚合
注: 聚合这个操作, 在上面操作中, 编译器已经帮我们自动导入了!!!!!
我们思考一个问题:
- 上面的各个模块是分开独立开发的,彼此互相独立,互补影响。假设如果现在
hx-dao模块更新升级了,那么其他模块是如何感知dao模块发生了变化的?
| ##container## |
|---|
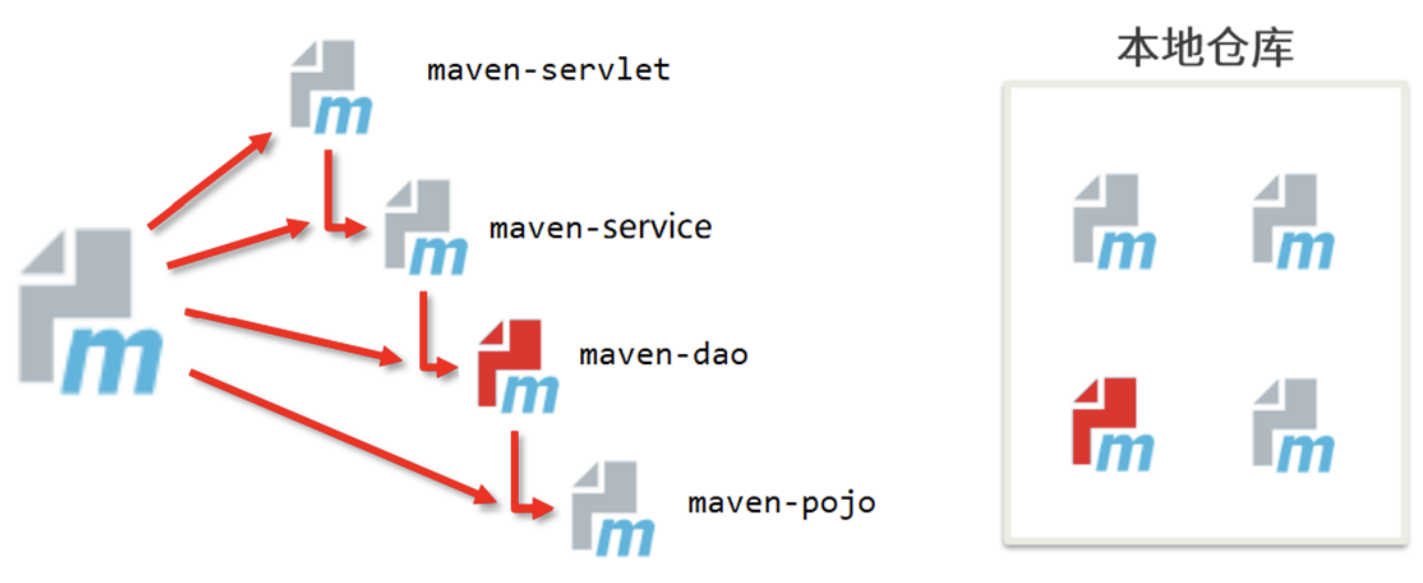 |
解决方案:
会不会有一个工程,专门对这些模块进行管理。对这些模块进行统一的编译,测试,打包等操作。一旦一个模块发生了变化,会同时对其他模块也进行编译、测试、打包。
此时就需要用到聚合的思想。
聚合的作用:用于快速构建maven工程,一次性管理多个模块。
例如:
父模块:
<packaging>pom</packaging> <!--定义打包方式-->
<modules>
<module>hx-dao</module>
<module>hx-pojo</module>
<module>hx-utils</module>
<module>hx-service</module>
<module>hx-servlet</module>
</modules>
子模块: 引入父工程
<parent>
<groupId>com.HX</groupId>
<artifactId>hx-main</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
此时在父模块执行生命周期会连带子模块一起编译等
问题:编译的顺序是怎么样的?
-
参与聚合操作的模块最终执行顺序与模块的依赖关系有关系。跟配置顺序没有关系。
-
各个模块的打包方式
- 父工程打pom
- Web工程打war包
- 其他工程 打jar包(如果没有任何打包配置,默认就是打jar包)
继承
通过继承可以实现在父工程中的配置,让子模块沿用思考。类似于java中的继承关系。
实现:
- 在子模块中,使用parent标签引入父工程,这样子工程和父工程就有了继承关系了
<parent>
<groupId>com.HX</groupId>
<artifactId>hx-main</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
优化分配
可以看到, dao层只用到了部分模块, 但把其他的jar包, 甚至tomcat都导入了
| ##container## |
|---|
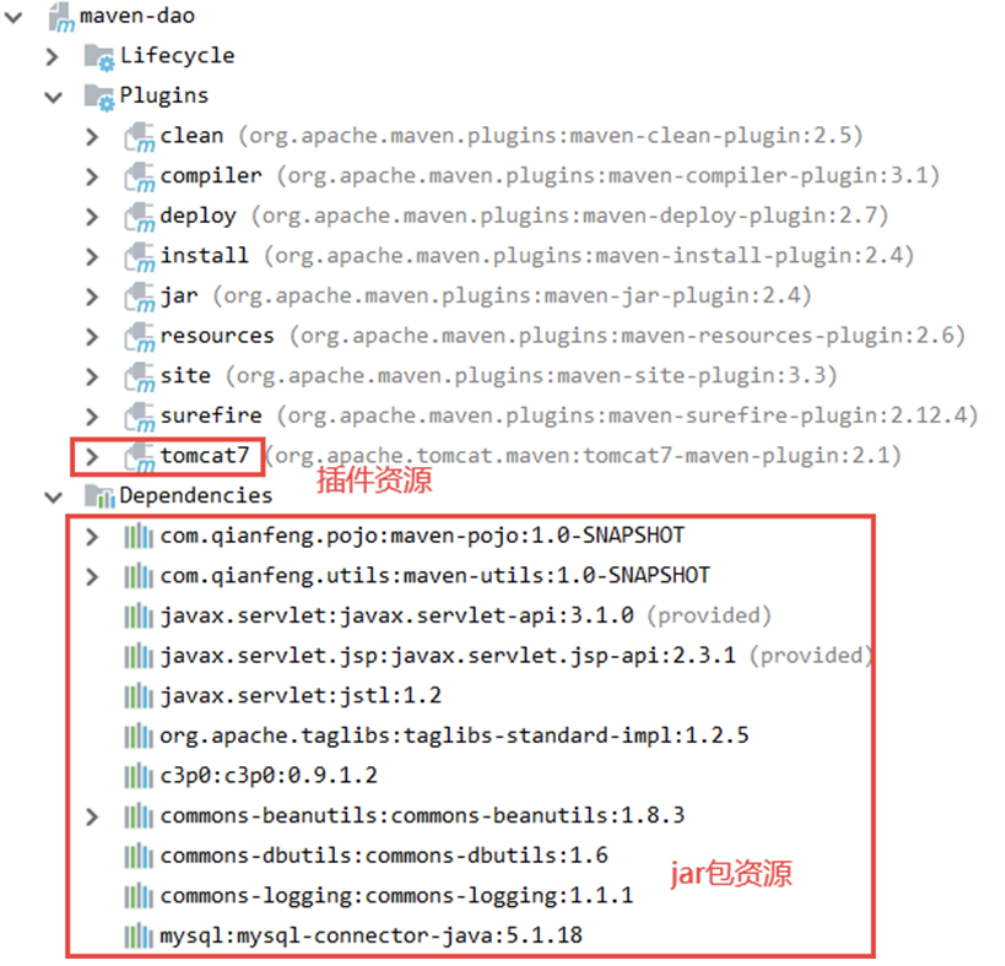 |
思考:这样的做法有没有问题?
答案:有,并不是子模块都需要所有父工程的资源。以maven-dao为例,这个子模块并不需要tomcat插件,也不需要servlet jsp相关的依赖。如果全部资源都继承下来会导致子模块特别大,将来打包,部署效率比较低。
解决方案:
- 使用
<dependencyManagement>标签帮我们管理依赖, 当然插件就使用<pluginManagement>来管理
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!-- ... -->
<!--logging-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.11</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<configuration>
<port>8088</port>
<path>/</path>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
hx-servlet节选
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.HX</groupId>
<artifactId>hx-service</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<!-- 同样不需要填写版本, 也不需要再次配置 -->
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
在子模块中按照自己的需求,引入对应的依赖,此时不需要加依赖的版本号了,因为在父工程里面已经给我们定义好了。
| ##container## |
|---|
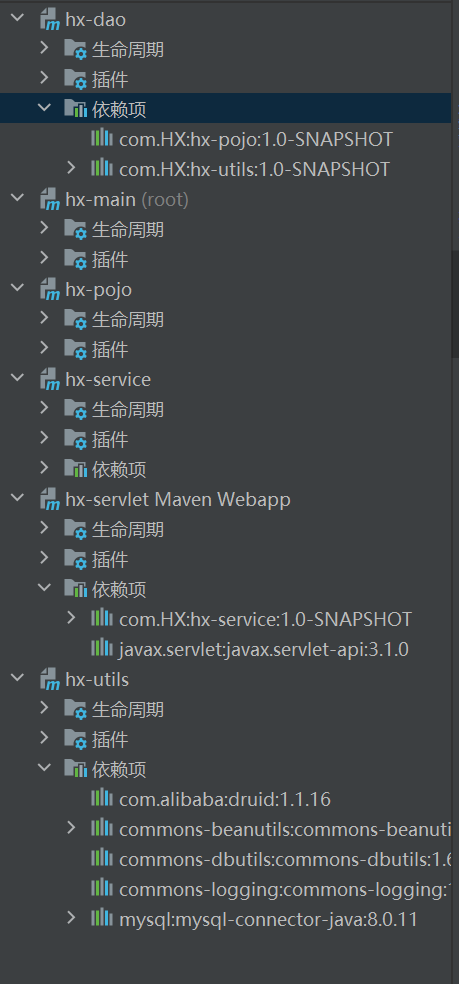 |
清晰, 精简多了!
总结
聚合和继承的关系
- 作用:
- 聚合用于快速构建项目
- 继承用于快速配置
- 相同点:
- 聚合与继承的
pom.xml文件打包方式均为pom。可以将两种关系定义在同一个pom文件中。 - 聚合和继承均属于设计系模块,并无实际的模块内容
- 聚合与继承的
- 不同点:
- 聚合是在当前模块中配置关系,聚合可以感知到参与聚合的模块都有哪些
- 继承是在子模块中配置关系,父模块无法感知哪些子模块继承了自己

